SITHERM 2714 Steel
Designation by Standards
Brand Name | Ravne | Mat. No. | DIN | EN | AISI/SAE |
SITHERM 2714 | UTOPEX2 | 1.2714 | 56NiCrMoV7 † | 55NiCrMoV7 | - |
Chemical Composition (in weight %)
C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | Ni | V | W | Others |
0.55 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 1.10 | 0.45 | 1.65 | 0.10 | - | - |
Description
Nickel hot work tool steel with good hardenability. Uniform hardness over section also at great dimensions. Resistance under impact loadings. Very good strength and toughness. Good tempering resistance and dimensional stability. Tools can be water or air cooled.
Applications
Forging tools, dies of all sorts, shapes and sizes, hot forging and pressing tools for steel and metal. Moulds, bushings, piercers etc.
Physical properties (average values) at ambient temperature
Modulus of elasticity [103 x N/mm2]: 215 Density [g/cm3]: 7.84
Thermal conductivity [W/m.K]: 36.0
Electric resistivity [Ohm mm2/m]: 0.30 Specific heat capacity[J/g.K]: 0.46
Thermal conductivity [W/m.K]
20oC | 500oC | 600oC |
36.0 | 36.8 | 36.0 |
Electric resistivity [Ohm mm2/m]
20oC | 500oC | 600oC |
0.30 | 0.70 | 0.84 |
Specific heat capacity[J/g.K]
20oC | 500oC | 600oC |
0.46 | 0.55 | 0.59 |
Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion 10-6 oC-1
20-100oC | 20-200oC | 20-300oC | 20-400oC | 20-500oC | 20-600oC | 20-700oC |
11.7 | 12.1 | 13.0 | 13.5 | 14.0 | 14.3 | 14.6 |
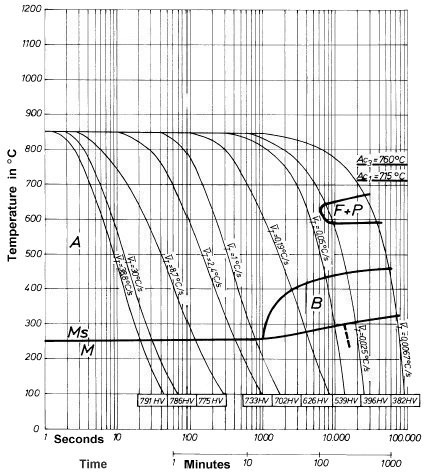
Continuous Cooling Transformation (CCT) Diagram
Soft Annealing
Heat to 650-700oC, cool slowly in furnace. This will produce a maximum Brinell hardness of 248.
Stress Relieving
Stress relieving to remove machining stresses should be carried out by heating to 650oC, holding for one hour at heat, followed by air cooling. This operation is performed to reduce distortion during heat treatment.
Hardening
Oil: Harden from a temperature of 830-870oC followed by oil quenching. Hardness after quenching is 58 HRC. Air: Harden from a temperature of 830-900oC followed by air quenching. Hardness after quenching is 56 HRC.
Tempering
Tempering temperature: See the data bellow.
Quenching in oil:
Tempering Temperature (oC) vs. Hardness (HRC) vs. Hardness (HRC) vs. Tensile Stregth (N/mm2)
100oC | 200oC | 300oC | 400oC | 450oC | 500oC | 550oC | 600oC | 650oC |
57 | 55 | 52 | 49 | 47 | 45 | 42.5 | 39 | 35 |
2140 | 1980 | 1790 | 1620 | 1530 | 1440 | 1345 | 1230 | 1110 |
Quenching in air:
Tempering Temperature (oC) vs. Hardness (HRC) vs. Hardness (HRC) vs. Tensile Stregth (N/mm2)
100oC | 200oC | 300oC | 400oC | 450oC | 500oC | 550oC | 600oC | 650oC |
55 | 53 | 50 | 47 | 45 | 43 | 40 | 37 | 32 |
1980 | 1845 | 1680 | 1530 | 1440 | 1360 | 1260 | 1170 | 1020 |
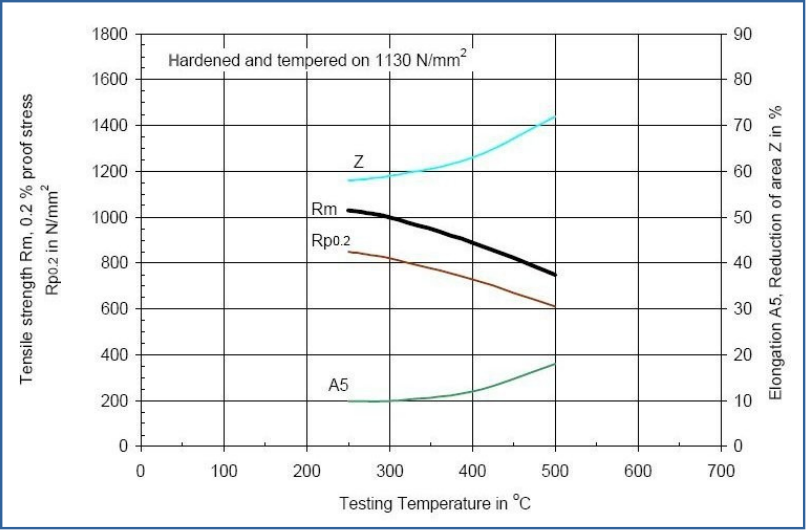
Tempering Diagram
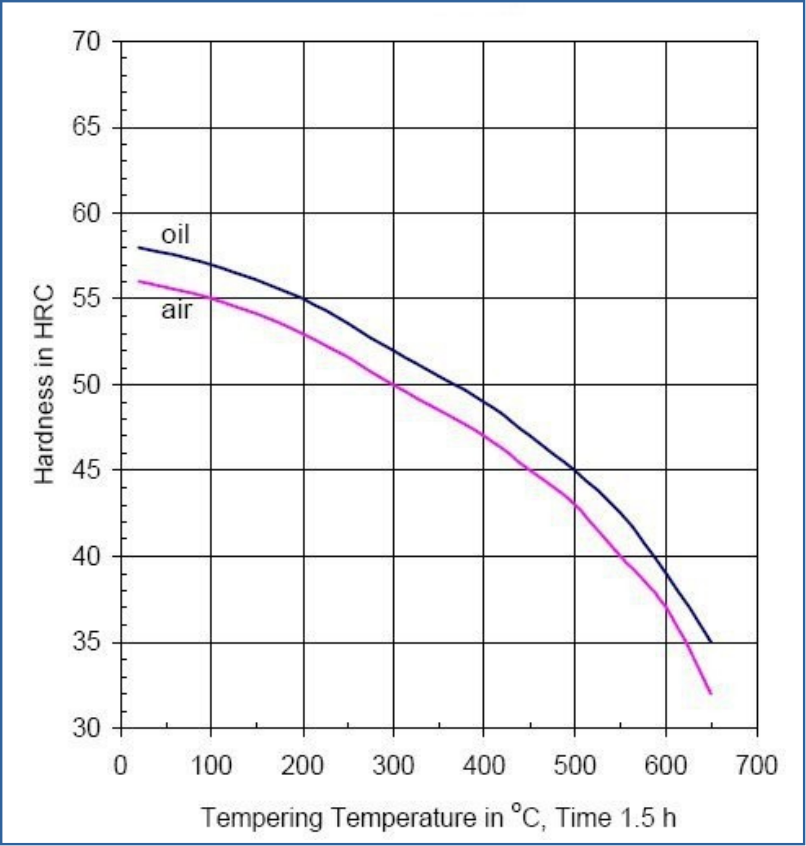
Diagram Tempering Temperature - Mechanical Properties
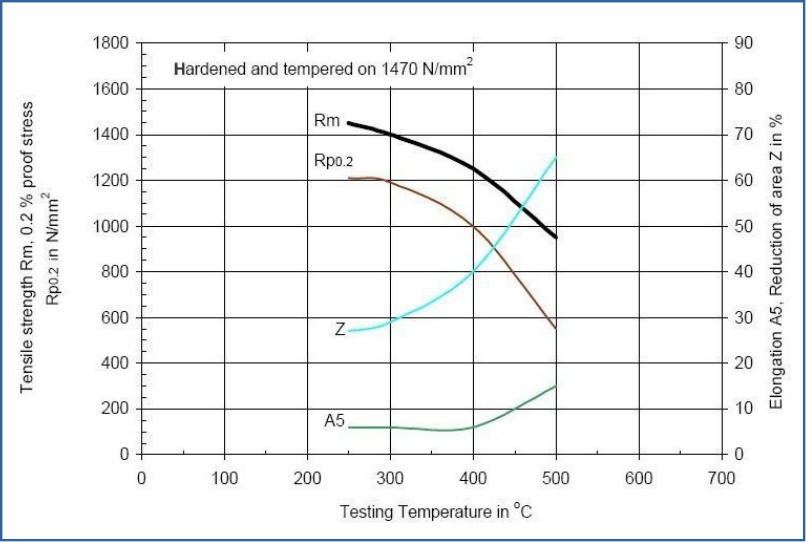
Diagram Tempering Temperature - Mechanical Properties
Forging
Hot forming temperature: 1050-850oC.
Machinability
The machinability rating of D3 is roughly 25 % that of free machining carbon steel 1018. Due to its abrasion resistant nature, machining in the hardened condition should be limited to finish grinding.
Forms manufactured: Please see the Dimensional Sales Program.
Disclaimer
The information and data presented herein are typical or average values and are not a guarantee of maximum or minimum values. Applications specifically suggested for material described herein are made solely for the purpose of illustration to enable the reader to make his own evaluation and are not intended as warranties, either express or implied, of fitness for these or other purposes. There is no representation that the recipient of this literature will receive updated editions as the become available.
Unless otherwise specified, registered trademarks are property of SIJ Metal Ravne company. Copyright 2016 by SIJ Metal Ravne d.o.o. All rights reserved. Contact our Sales Office for more information.